

Next: 4 File Specifications
Up: Sturmian Bound-state and Scattering
Previous: 2 Solution of coupled
Subsections
FORTRAN 90 namelist input in all cases.
In the descriptions below, R=real, I=integer, L=logical, S=string with ' ' marks.
Arrays are indicated by dimensions, e.g. (1:2).
The notation [R;0.05] Means a real variable with default value 0.05.
&mefile fpot = '1-_l1s0j1t' /
&sturmin
Eo(1)=-1.0 egsmin=-1.0 egsmax=+0.0 sturm(1)='T' nsturm=20,
stepi = 0.05, rmax=20, wfrmax=40
ebeg=0.5 estep=-0.5 emax=5.0 /
- fpot
- [S]: Input files are fpot.spec for channel specifications,
fpot.mel for matrix elements, and fpot.occ for forbidden-state projection
operators. After some header information in the spec file,
successive
 sets are concatenated in all these files.
sets are concatenated in all these files.
- potcoef(1:npots)
- [R;npots*1.0] Coefficients of the npots different
potential components in the fpot.mel file. (New in version 83)
- kdiag,vdiag(1:2),rdiag(1:2),adiag,nidiag [I,5*R,I; 3,5*0.,0]
- Diagonal potential to add
to all channels. kdiag=0 for Coulomb, 1 for Woods-Saxon,
2 for Gaussian and 3 for regularised inverse cubic
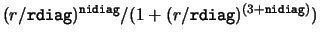 .
.
Use vdiag(1),rdiag(1) for first  set,
and vdiag(2),rdiag(2) for all others.
set,
and vdiag(2),rdiag(2) for all others.
- Eo(1:2)
- [R; 0.,0.]: Energy for sturmians or for logarithmic derivatives
Use Eo(1) for first 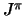 set, and Eo(2) for all others.
set, and Eo(2) for all others.
- sturm(1:2)
- [S; 'F','F']:
T=Calculation using sturmian basis;
F=Use basis of energy eigenstates in each channel's diagonal potential;
L=Use Laguerre orthonormal basis.
Use sturm(1) for first 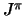 set, and sturm(2) for all others
set, and sturm(2) for all others
Use only sturm='F' when scattering required.
- simeq
- [L;F] Use linear-equations method to find R-matrix for just
one scattering energy, ignoring all eigenvalues.
- egsmin
- [R;-1] Lower bound on energy of eigenvalues to examine in detail.
- egsmax
- [R;0.] Upper bound on energy of eigenvalues to examine.
- ngsmax
- [I;0] Number of eigenvalues to find:
If ngsmax = 0, find all eigenvalues by complete diagonalisation,
If ngsmax = 1 or (estep<0 and this is the first 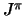 set):
set):
use inverse iteration to find eigenstate nearest to egsmin,
If ngsmax = 2 ... 25% of all eigenvalues, use diagonalisation and
bisection search to find eigenstates in interval [egsmin,egsmax].
Warning: scattering calculations are only accurate up to
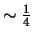 of
maximum eigenenergy found.
of
maximum eigenenergy found.
If ngsmax > 25% of all eigenstates, find them all by complete diagonalisation.
- meigs
- [I;0] Maximum number of eigenvectors to store for a
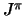 . If zero,
store all eigenvectors.
. If zero,
store all eigenvectors.
- eeigmax
- [R;5000. for 2-body, else 50.] Maximum energy of eigenvector to find for a
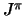
- maxset
- [I;0] Maximum number of
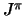 sets to be solved. If zero,
solve for all sets.
sets to be solved. If zero,
solve for all sets.
- rmax
- [R;20.] Maximum radius, used for R-matrix calculations. All couplings up
to rmax are always included.
- numax
- [I;3] Maximum power
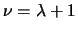 for exterior
for exterior 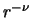 extrapolations of exterior coupling potentials.
extrapolations of exterior coupling potentials.
- wfrmax
- [R;40.] Maximum radius for wave functions for bound states and matrix elements.
Asymptotic forms are used if necessary to extrapolate beyond rmax.
- rafin
- [R;20.] If rafin > rmax, use asymptotic methods for the radial range rmax <r< rafin.
rafin may be extended up to rafix if necessary for convergence.
- stepi
- [R;0.05] Radial step size for basis states
- steps
- [R;1.0] Radial step size for storing bound and continuum wave functions.
- tinside
- [R;-1] If positive, start radial integrations at this distance
inside a classical turning point. If starting point is greater than
rmax, use uncoupled ADW approximation for the R-matrix,
and omit the interior diagonalisation. (You must use asymptotic
methods in order then to get non-zero phase shifts!)
- lprwf
- [I;1] Printing wavefunctions. 0=none; 1=bound-state wfns in file 11;
2=diagonal continuum wfs in file 9;
3=all continuum wfs in file 8.
- mlpr
- [I;1] Maximum L/K value of channel to print when lprwf=3
- prns
- [L;F] Print norm matrix for Faddeev equations
- fadex
- [I;1] Number of Faddeev components to use for solutions
- nsturm
- [I;20] Number of basis states for each channel,
which have 1...nsturm nodes.
If nsturm=0, then start with ADW R-matrix at rmax.
- pertcent
- [L;F] Move centrifugal barrier from basis potentials to perturbation
(useful for strong couplings), so all channels have the same set of
radial basis functions.
- cutl
- [R;1.6] See cutr.
- cutr
- [R;0] Lower radius for counting nodes of basis wave functions
is max(cutr,cutl*stepi*L).
- pralpha
- [L;F] Print alpha(*) for each basis state to file 4,
details of searching for basis states to file 2.
- pripot
- [L;F] Print all coupling potentials to file 3.
- prsturm
- [L;F] Print basis wave functions in file 160+channel number
- prmats
- [L;F] Print normalisation matrix MM and Hamiltonian matrix AA
in file 6.
- Vsturm
- [R;-50.] Depth of central potential for Sturmians.
- rsturm
- [R;1.2] Reduced radius r0 for Sturmian potential
- asturm
- [R;0.6] Diffuseness a for Sturmian potential.
- A
- [R;10.] Use WS radius
R = r0 A1/3 for Sturmian potential.
- kind
- [I;9] Kind of Sturmian potential:
0=Coulomb, 1=Woods-Saxon,
2=Channel diagonal potential, 3=Constant (-1), 4=read in file 36,
5=r-3 shape, 6=lowest eigenenergy surface,
9=Coulomb(0) for sturm='T' and diagonal(2) for 'F'.
(If kind=2, the diagonal potentials must all be sufficiently attractive).
- ebeg
- [R;0.1] First scattering energy (MeV).
- estep
- [R;0.1] Average increment in energy. The energies used will actually be
linear in
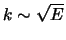 .
.
- emax
- [R;0.0] Maximum scattering energy
- elinear
- [L;F] Linear E steps, rather than linear in k.
- rmaxsc
- [R;0.0] Maximum radius for scattering
 sets. If zero, use rmax.
sets. If zero, use rmax.
- nogscat
- [L;F for 2-body, else T] no scattering for first
 set. Such scattering
is also disabled by estep<0.
set. Such scattering
is also disabled by estep<0.
- Buttle
- [I;5] 0=no Buttle correction; Buttle=number of interpolation points
between poles of uncoupled problem. Buttle=5 usually sufficient.
If Buttle<0, do `exact energy' rather than interpolated correction.
Note: Buttle corrections only available with energy eigenstate
basis (sturm=F), so scattering calculations only advised
with that basis.
- prbut
- [L;F] Print details of Buttle corrections
- prrm
- [L;F] Print R-matrix for each energy in file 6.
- prkm
- [L;F] Print K-matrix for each energy in file 6.
- prtm
- [L;F] Print S-matrix for each energy in file 6.
- prtran
- [L;F] Print details of B(Ek) calculations
- nftt
- [I;0] File number for binary storage of S/T-matrix elements
- minnop
- [I;6] Minimum number of channels with plane waves, if more than this number of channels
- maxnop
- [I;20] Maximum number of channels with plane waves.
- turnmax
- [R;-40] Minimum turning point distance to keep a channel. If <0, keep all.
- rinte
- [R;10.] Radius for integration of diagonal wfs to get `interior norms'
- e1only
- Calculate only B(E1,2) g.s.
 E matrix elements,
and not any continuum wavefunctions. Only effective if no asymptotic propagations.
E matrix elements,
and not any continuum wavefunctions. Only effective if no asymptotic propagations.
- wfs
- [L;F] Calculate continuum wavefunctions in steps of steps (slow)
(Set true, if strfun or rtrans > htrans).
- strfun
- [L;F] Calculate `strength functions' in steps of steps (slower)
- discrete
- [L;F] Calculate discrete responses to discretised-continuum eigenstates
- htrans,rtrans
- [R,R; 0.1,0.] If rtrans > htrans, calculate gs to continuum
transition densities in radial steps of htrans up to rtrans (slowest)
- prrexp
- [L;F] Print R-matrix, Buttle parameters and asymptotic couplings powers in files 150
Asymptotic propagators are only used if rafin > rmaxsc,
and for scattering require Eo = 0.
- xlrgs
- [L;T] Apply to bound state searches too.
- ewron
- [R;10-6] The error in the multichannel Wronskian must be less than ewron for all
channels for convergence of the asymptotic wavefuncion. The
smaller that ewron is set the larger the radius of convergence
and the distance of propagation.
- betalw
- [R;10-6] Accuracy parameter for Light-Walker propagators
- prwr
- [L;F] Print Wronskian errors
- rafix
- [R;105] Absolute maximum radius for evaluating Gailitis expansions
- rfact
- [R;1.2] Fractional increment to radius for trial evaluation of Gailitis expansions,
if the test on the Wronskian fails.
- gfact
- [R;.3] Factor which decides whether the final radius, rafin, should be
the value estimated for the current energy or the value at
which the previous energy converged. If the ratio of the maximum
coefficient in the Gailitis expansion for the current energy
to that of the previous energy is > gfact the radius for the
previous energy is taken.
- maxtry
- [I;100] Maximum number of increments for trial evaluation of Gailitis expansions
- degeny
- [R;10-5] Thresholds closer than degeny will be taken as
degenerate. With small threshold differences
solutions converge at large radii resulting in large
propagation distances.
- cuplim
- [R;0.] Closed channels with a coupling with open channels less
than cuplim may be dropped during propagation by the LW method.
- deplim
- [R;0.] Closed channels more deeply bound than deplim may be
dropped during propagation by the LW method.
- flwp
- [S,'lwra'] File name for scratch storage of LW sectors
- flwpr
- [S,'lwrmats'] File name for scratch storage of LW global propagators
- idiscr
- [I;71] File number for flwp; idiscr+1 is file number for flwpr.
- prwf
- [L;F] Print wave functions after global propagations
- prbc
- [L;F] Print bound-state combination coefficients
- debug
- [L;F] Information of LW propagators.
- prntv
- [L;F] Print local diagonalisations for LW method
- apflg(1:5)
- [I;0,0,0,1,0] For debug prints in GAL library:
- iapflg(1)
- =1 print expansion coefficients in subroutine GAILCO.
- iapflg(2)
- =1 NOT USED.
- iapflg(3)
- =1 print asymptotic wavefunctions.
- iapflg(4)
- =1 calculate errors in the wavefunctions and print if greater
than apeps described next.
- apeps
- [R;10-6] Errors in the wavefunctions greater than apeps are printed
under the debug flag apflg(4).
- ipflg
- [I;0] Print information on Gailitis expansions
- iasy
- [I;50] Number of terms in expansion of asymptotic wave function (An
even number). This number depends on the largest floating point
number possible on the machine. If overflow is about to occur the
program stops with the instruction to reset iasy to a smaller value.
- ncol
- [I;10] Number of columns for printing some matrices
- msurf
- [I;0] Do Not use
- mblock
- [I;0] Do Not use
- efermi
- [R;0.] Do Not use
Bound state asymptotic propagators are only used if xlrgs,
if rafin > rmax,
if no bound state has yet been found, and if the interior diagonalisation has found
a negative-energy eigenstate.
The bound-state asymptotic propagators can use any Eo value.
- emin
- [R;egsmin] Minimum bound state energy
- emax
- [R;egsmax] Maximum bound state energy
- ne
- [I;10] Number of energy points in first scan. Use bisection if determinant is
found to change sign between any two of these points.
- eps
- [R;10-5] Accuracy criterion to terminate bisection search
- kpole
- [I;1] Look for bound state near eigenstate number kpole of interior diagonalisation.
- idiag
- [I;1] Trace details of bound-state search
- ibslt
- [I;ngsmax] Number of bound states to find
- numaxgs
- [I;4] Maximum power
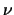 of
of 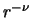 couplings included in
Gailitis expansions for bound states.
couplings included in
Gailitis expansions for bound states.


Next: 4 File Specifications
Up: Sturmian Bound-state and Scattering
Previous: 2 Solution of coupled
Prof Ian Thompson
2004-10-19